(Picture generated by ChatGPT with user prompt)
Why SEO Feels Complicated — and Why It Doesn’t Have to Be
If you’re a small business owner or entrepreneur, chances are you’ve heard the phrase “you need SEO.” Maybe you’ve even tried researching it yourself, only to feel overwhelmed by technical language, expensive tools, and conflicting advice.
The reality is much simpler.
You don’t need to become a digital marketing expert to benefit from search engine optimization. You just need to understand a few foundational strategies that help customers find your business online.
SEO works because it connects you with people who are already searching for what you offer. Unlike traditional advertising, which interrupts audiences, SEO meets customers at the exact moment they need a solution.
This blog breaks down 10 simple SEO wins you can implement this week to improve visibility, attract more customers, and build long-term online growth.
What SEO Really Means for Small Businesses
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the process of improving your online presence so search engines like Google can understand your website and show it to the right audience.
For small businesses, SEO focuses on three main goals:
- Helping local customers discover your services
- Making your website easier to understand and navigate
- Building trust through helpful, relevant content
When done correctly, SEO becomes one of the most cost-effective marketing strategies available. Instead of paying for every click, you earn visibility organically over time.
According to Google Business resources, optimized business listings significantly improve local discovery and engagement:
https://www.google.com/business/
Why Entrepreneurs Should Care About SEO
Small businesses often compete with larger brands that have bigger marketing budgets. SEO helps level the playing field.
Here’s why SEO matters:
- Customers research before purchasing
- Local searches often lead to immediate action
- Organic traffic builds credibility
- SEO works continuously, even when you’re not marketing
Think of SEO as building a digital storefront. The clearer and more welcoming it is, the more customers walk through the door.
🚀 10 Simple SEO Wins You Can Do This Week
SEO doesn’t have to be complicated or expensive. In fact, a few small changes can dramatically improve how customers find your business online.
Here are 10 quick SEO wins you can start today — no marketing degree required.
⭐ 1. Claim Your Google Business Profile (Your #1 SEO Priority)
If your business isn’t optimized on Google, you’re missing local customers every day.
Your Google Business Profile helps you appear in:
- Google Maps
- Local search results
- “Near me” searches
Make sure your profile includes:
✔ Correct contact information
✔ Updated hours
✔ Service areas
✔ High-quality photos
✔ Customer reviews
👉 Set yours up here:
https://www.google.com/business/
Pro tip: Businesses with reviews get more clicks and more trust.
🔎 2. Focus on ONE Keyword Per Page
Trying to rank everything usually means ranking for nothing.
Instead, choose one clear keyword per page.
✅ Better: “Family photographer in Boston”
❌ Worse: “photography services”
Specific searches bring customers who are ready to buy — not just browse.
🧠 3. Upgrade Your Page Titles & Descriptions
Your search result listing is your first impression.
Strong titles:
- Clearly explain what you offer
- Include your keyword naturally
- Make people want to click
Think of it like a mini advertisement for your website.
Small edits here = big traffic improvements.
📱 4. Make Sure Your Website Works on Mobile
Most customers visit your website from their phones.
If your site is slow or hard to use, they leave — fast.
Your site should:
- Load quickly
- Be easy to read
- Have clickable buttons
- Navigate smoothly
Test it instantly:
https://search.google.com/test/mobile-friendly
🧩 5. Use Headings to Make Content Easy to Read
People scan before they read.
Break content into sections using:
- H1: Main topic
- H2: Key sections
- H3: Supporting points
Clear structure keeps visitors engaged and helps Google understand your content.
✍️ 6. Post Helpful Content Once a Month
You don’t need to blog every week.
One helpful article per month can dramatically improve SEO.
Start with the questions customers already ask:
- “How do I choose the right service?”
- “What should I expect?”
- “Common mistakes to avoid”
Helpful content builds trust — and trust builds sales.
🔗 7. Add Internal Links (Your Secret SEO Boost)
Guide visitors through your website.
Link:
- Blog posts → services
- Services → contact page
- Homepage → key offers
Internal links help Google crawl your site and keep visitors on your site longer.
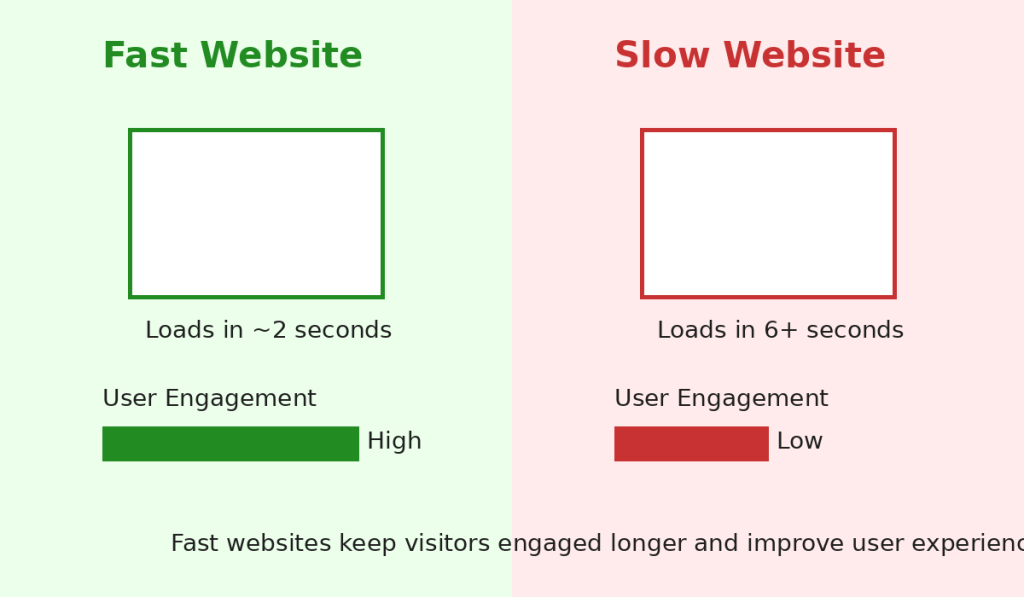
⚡ 8. Speed Up Your Website
Slow websites lose customers.
Improve speed by:
- Compressing images
- Removing unused plugins
- Using reliable hosting
Check your speed here:
https://pagespeed.web.dev/
Even a 1–2 second improvement can increase conversions.
📍 9. Get Listed Everywhere Online
Search engines trust businesses that appear consistently across the web.
Create listings on:
- Yelp
- Facebook Business
- Local directories
- Industry platforms
Keep your business name, address, and phone number identical everywhere.
Consistency = credibility.
📊 10. Track What’s Working
Marketing without tracking is guessing.
Use free tools like:
- Google Search Console
- Google Analytics
These tools show:
✅ What people search
✅ Where traffic comes from
✅ Which pages perform best
Review results monthly and adjust as you grow.
💡 Quick Reminder
SEO success isn’t about doing everything perfectly.
It’s about doing small things consistently.
Start with one step this week. Then another next week. Momentum builds faster than you think.
Common SEO Mistakes Small Business Owners Make
Even motivated entrepreneurs can unintentionally slow their growth.
Avoid these mistakes:
- Targeting overly broad keywords
- Copying competitor content
- Ignoring local optimization
- Publishing content inconsistently
- Forgetting calls to action
SEO rewards clarity and consistency more than complexity.
Why SEO Is a Long-Term Investment
Unlike paid ads, SEO compounds over time.
Each improvement strengthens your digital presence:
- More content builds authority
- Better structure improves rankings
- Consistency increases trust
While results may take weeks or months, the long-term payoff is sustainable growth.
Final Thoughts
SEO doesn’t require advanced technical skills or a massive marketing budget. It requires understanding your customers and making your business easy to find online.
By consistently applying these ten strategies, small business owners can increase visibility, build credibility, and attract customers actively searching for their services.
Small actions today lead to long-term digital growth tomorrow.
Ready to take the next step?
Our agency offers a free 15-minute SEO audit where we identify quick wins and create a simple action plan tailored to your business.
👉 Schedule your free SEO audit today and start showing up where your customers are searching.